Physics - Waves and Oscillations
Classification of Waves

Based on the direction of propagation, waves are classified as transverse and longitudinal. The transverse wave is a wave that travels in a direction perpendicular to the surface of the medium, while a longitudinal wave travels in a direction parallel to the surface of the medium.
In general, transverse waves are waves that have a wavelength much greater than the thickness of the medium. Longitudinal waves are waves that have a wavelength much less than the thickness of the medium. Transverse waves can be further subdivided into surface waves, which are waves that travel in the surface of the medium, and volume waves, which are waves that travel in the volume of the medium.
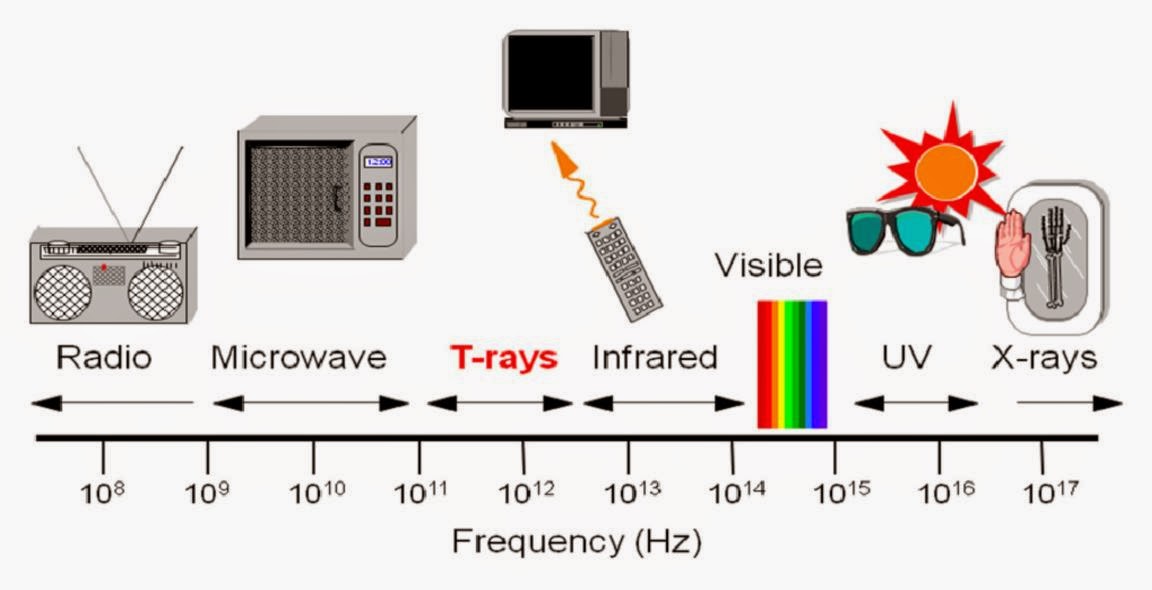 Figure 2. Electromagnetic waves | Fair use (hebasoffar.blogspot.com)
Figure 2. Electromagnetic waves | Fair use (hebasoffar.blogspot.com)
Based on the medium, waves are classified as mechanical and electromagnetic. Mechanical waves travel through a medium such as water or air. Electromagnetic waves propagate through a vacuum. Examples of mechanical waves are sound and ultrasound. Light and radio waves are examples of electromagnetic waves.
Difference Between Waves and Oscillations
It’s important to note that an oscillation is not the same as a wave, but an oscillation can be the cause of a wave. An oscillation is a kind of movement that is repeated at regular intervals under certain conditions. An example of an oscillation is the motion of a pendulum, it moves back and forth, but it does not move in a wave-like way.
Parts of Longitudinal and Transverse Waves
 Figure 3. Parts of longitudinal waves | Own work
Figure 3. Parts of longitudinal waves | Own work
 Figure 4. Parts of transverse waves | Own work
Figure 4. Parts of transverse waves | Own work
6 Properties of Waves
- reflection: waves can reflect on impenetrable surfaces
- refraction: waves can be refracted when they pass from one medium to another
- dispersion: waves can be dispersed into separate frequencies when they pass through dispersive medium
- diffraction: waves can be diffracted when they pass through openings
- interference: waves can interfere with each other
- polarization: waves can be polarized and their polarization can be changed by passing through a polarizer